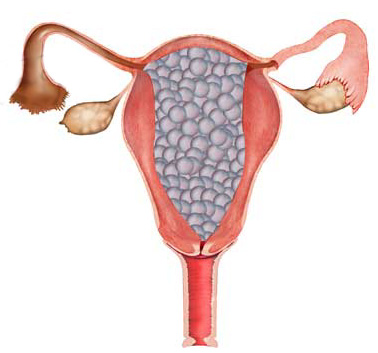
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease/Complete h-mole
§Hydatidiform mole
§
§Incomplete or partial mole
§
§Coexisting mole and fetus
§
§Invasive mole
§
§Choriocarcinoma
Complete mole
-Fertilization an empty egg by one sperm.
-All placental villa swollen.
-Fetus, cord, amniotic membrane are absent.
-Paternal chromosomes only. 46 XX.
-diploidy

incomplete mole
-fertilization of an egg by
two sperms
-some placental villa swollen
Fetus, cord, amniotic
membrane are present
-Paternal and maternal 69XXY
-Triploid
◦Heavy Vaginal bleeding, excessive vomiting, & high BP .
◦
◦a large-for-date uterus with “swiss cheese” endometrium
◦
◦Serum HCG titers will be markedly elevated.
◦
◦Large cysts may be seen in the ovaries : theca lutein cysts

Complete h-mole
Most common type of GTN
(GTN, also known as choriocarcinoma).
Proliferative growth of trophoblastic tissue
May become invasive or metastatic : invasive mole, chriocarcinoma